Vitamin B12 deficiency is a condition that occurs when the body does not have enough vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that is involved in the production of red blood cells and in the proper functioning of the nervous system.
Editor's Notes: Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment have published 5 May, 2023. Vitamin B12 deficiency is a serious condition that can lead to a variety of health problems. If you think you may be deficient in vitamin B12, it is important to see your doctor to get tested and treated.
We all know that Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient for our body. But what happens when we don't get enough of it? After doing some analysis, digging deep into information, we made Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment we put together this Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Key differences or Key takeaways:
| Key | Takeaways |
|---|---|
| Causes | Vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by a variety of factors, including: |
| Symptoms | The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency. |
| Treatment | Treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency involves taking vitamin B12 supplements. |
Transition to main article topics:
- Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Treatment of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
FAQ
This FAQ section addresses common questions and provides additional insights on vitamin B12 deficiency.
Question 1: What are the most common causes of vitamin B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can arise from various causes, including inadequate dietary intake, impaired absorption due to gastrointestinal issues, and certain medications that interfere with vitamin B12 absorption.
Question 2: Can vitamin B12 deficiency lead to serious health problems?
Yes, untreated vitamin B12 deficiency can have significant health implications. It can cause anemia, nerve damage, and cognitive impairment if left unaddressed.
Question 3: How is vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a medical history review, physical examination, and blood tests to measure vitamin B12 levels.
Question 4: What are the treatment options for vitamin B12 deficiency?
Treatment typically involves vitamin B12 supplementation in the form of injections or oral tablets. The frequency and dosage will depend on the severity of the deficiency.
Question 5: Can vitamin B12 deficiency be prevented?
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vitamin B12 sources like meat, fish, and fortified foods can help prevent deficiency. Individuals with certain risk factors may require supplementation.
Question 6: What are the key takeaways regarding vitamin B12 deficiency?
It is crucial to be aware of the potential causes and consequences of vitamin B12 deficiency. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can help prevent serious health issues. Regular monitoring and appropriate supplementation are essential for individuals with known risk factors or those following restrictive diets.
See the next section for more information on vitamin B12 deficiency.
Tips
Vitamin B12 is essential for DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, and neurological function.Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment Identify and address a deficiency to preserve optimal health.
Tip 1: Consume Animal-Based Foods
Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, and milk are abundant in vitamin B12. Include these items in your diet regularly to ensure adequate intake.
Tip 2: Supplement if Necessary
Vegans, vegetarians, and individuals with malabsorption disorders may require B12 supplements. Consult a healthcare professional for guidance on dosage and appropriate forms.
Tip 3: Get Regular Blood Tests
Mild deficiency can present without noticeable symptoms. Periodic blood tests can detect low levels and enable timely intervention.
Tip 4: Address Underlying Causes
Identify and manage underlying conditions that impair vitamin B12 absorption, such as pernicious anemia or gastrointestinal disorders.
Tip 5: Treat Without Delay
Untreated B12 deficiency can lead to severe consequences. Seek medical attention promptly for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Summary: Early detection and intervention are crucial in addressing vitamin B12 deficiency. By following these tips, individuals can proactively protect their health and well-being.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a common condition that can lead to a variety of health problems. It is important to be aware of the causes, symptoms, and treatment of vitamin B12 deficiency in order to prevent or manage this condition.
- Causes: Pernicious anemia, dietary deficiency
- Symptoms: Fatigue, weakness, pale skin
- Diagnosis: Blood test, physical exam
- Treatment: Vitamin B12 supplements, injections
- Prognosis: Good with treatment
- Complications: Neurological damage, heart disease
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on your health. However, it is a treatable condition, and with proper treatment, you can prevent or manage the symptoms and prevent serious complications.
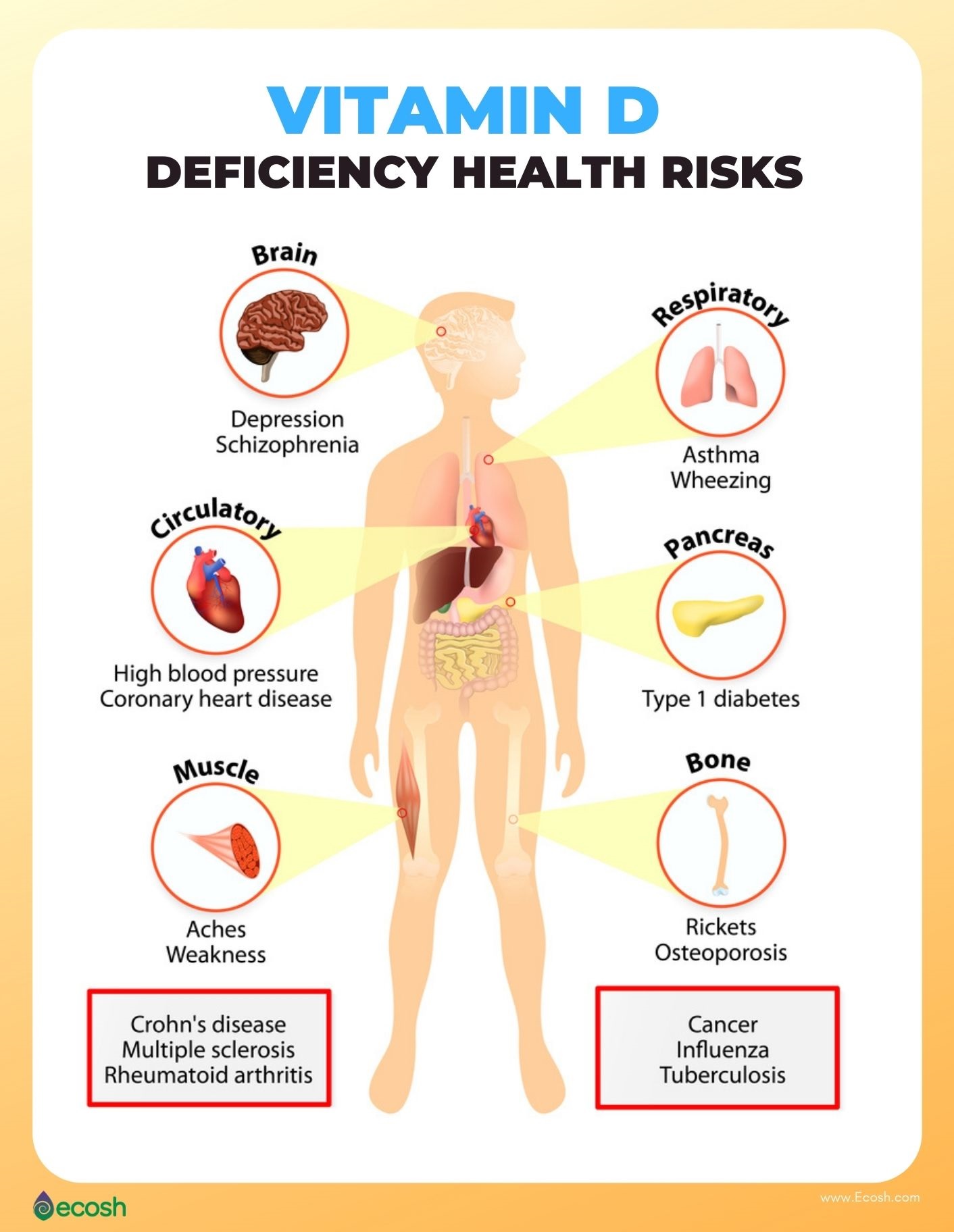
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY (VDD) - Symptoms, Causes, Risk Groups and 11 - Source ecosh.com
Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in the body's metabolism, nerve function, and blood cell production. A deficiency of vitamin B12 can lead to a variety of health problems, including fatigue, anemia, and neurological damage.

Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment - Source plantbaseddiets.in
There are several factors that can contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency, including:
- Inadequate dietary intake: Vitamin B12 is found naturally in animal products, such as meat, fish, and poultry. People who do not eat enough of these foods may be at risk for deficiency.
- Malabsorption: Vitamin B12 is absorbed in the small intestine. Conditions that affect the absorption of vitamin B12, such as celiac disease or Crohn's disease, can lead to deficiency.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as metformin and proton pump inhibitors, can interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12.
The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet
- Difficulty concentrating
- Memory loss
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor to rule out vitamin B12 deficiency. Vitamin B12 deficiency can be diagnosed with a simple blood test.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 deficiency is a serious condition that can lead to a variety of health problems. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent or minimize the risk of complications.
If you think you may be at risk for vitamin B12 deficiency, talk to your doctor. They can recommend ways to increase your intake of vitamin B12 and, if necessary, prescribe supplements.
